In the ever-evolving landscape of business, the need for adaptability and rapid iteration has become more crucial than ever. This is where lean business planning comes into play.
A lean business plan is a streamlined and simplified version of a traditional business plan. It is a one-page document that is designed to be concise and focused, making it easier for entrepreneurs and small business owners to develop, communicate, and implement their business strategies.
Lean business planning has gained popularity in the business world as an effective approach for startups to iterate their ideas faster, find a working business model, and ultimately succeed in the market.
Although some existing businesses use lean business planning when they have ideas or strategies for growth and expansion that they need to quickly test, lean business plans are ideal for startups. It assists startup businesses that have yet to identify a working business model in doing so faster because it involves a lot of testing of assumptions and ideas.
In this article, we explore the benefits of lean business plans over traditional ones and provide insights into the process of creating a lean business plan.
Benefits of Lean Business Plans Compared with Traditional Business Plans
Before we get into the specifics of creating a lean business plan, let us look at some of the advantages it has over traditional, lengthy business plans.
1. Simple and Efficient
Traditional business plans often involve extensive documentation, lengthy market research, and complex financial projections. On the contrary, lean business plans focus on the essentials, emphasizing simplicity and efficiency. By cutting down unnecessary details, business owners can quickly outline their vision, strategy, and key tactics.
Imagine you have a brilliant business idea that you’re excited to execute. With a lean business plan, you can jot down the core components of your plan on a single page, keeping the process smooth and hassle-free.
2. Rapid Iterations
In a rapidly changing business landscape, the ability to iterate and adapt is crucial. Lean business plans are designed to be flexible, allowing entrepreneurs to make swift adjustments based on market feedback and emerging trends. This agile approach enables businesses to stay ahead of the competition and maintain relevance with their target audience.
Consider the success stories of tech giants like Google, Facebook, Amazon, and Airbnb. They have all utilized lean business planning techniques to test their ideas quickly, make improvements, and scale their operations efficiently.
3. Cost-Effective
Traditional business plans can be time-consuming and expensive to create. In contrast, lean business plans are cost-effective, requiring fewer resources and saving precious time. This lean approach is especially beneficial for startups and small businesses, allowing them to allocate their resources more efficiently.
4. Adaptability
One of the key aspects of lean business planning is its adaptability. As the business landscape evolves, entrepreneurs can readily adjust their strategies and tactics to meet new challenges. This adaptability empowers businesses to pivot when necessary and explore alternative approaches to achieving success.
5. Action-Oriented
A lean business plan is not just a static document. It serves as a roadmap for action. And as a business, you need to take action to validate your strategies. A lean business plan helps you do this. It outlines clear objectives, actionable steps, and measurable goals, inspiring business owners and their teams to take purposeful and decisive actions. The focus on actionable insights enhances productivity and fosters a results-driven culture within the organization.
The Process of Lean Business Planning
Now that we understand the compelling advantages of lean business plans, let’s delve into the process of creating one. Contrary to extensive traditional business plans, a lean business plan can be succinctly summarized on a single page.
The process involves four stages:
- Create your plan
- Run it to test
- Review the result
- Revise your plan
If you are a startup, this process helps you quickly test your assumptions to validate them and find out what works and what doesn’t. Choosing the lean business planning methodology can help you minimize risk and avoid wasting resources.
If you are an existing business, lean business planning helps you develop and implement new strategies that bring you closer to your business goals over a period of time.
So how do you create a lean business plan? Let’s find out!
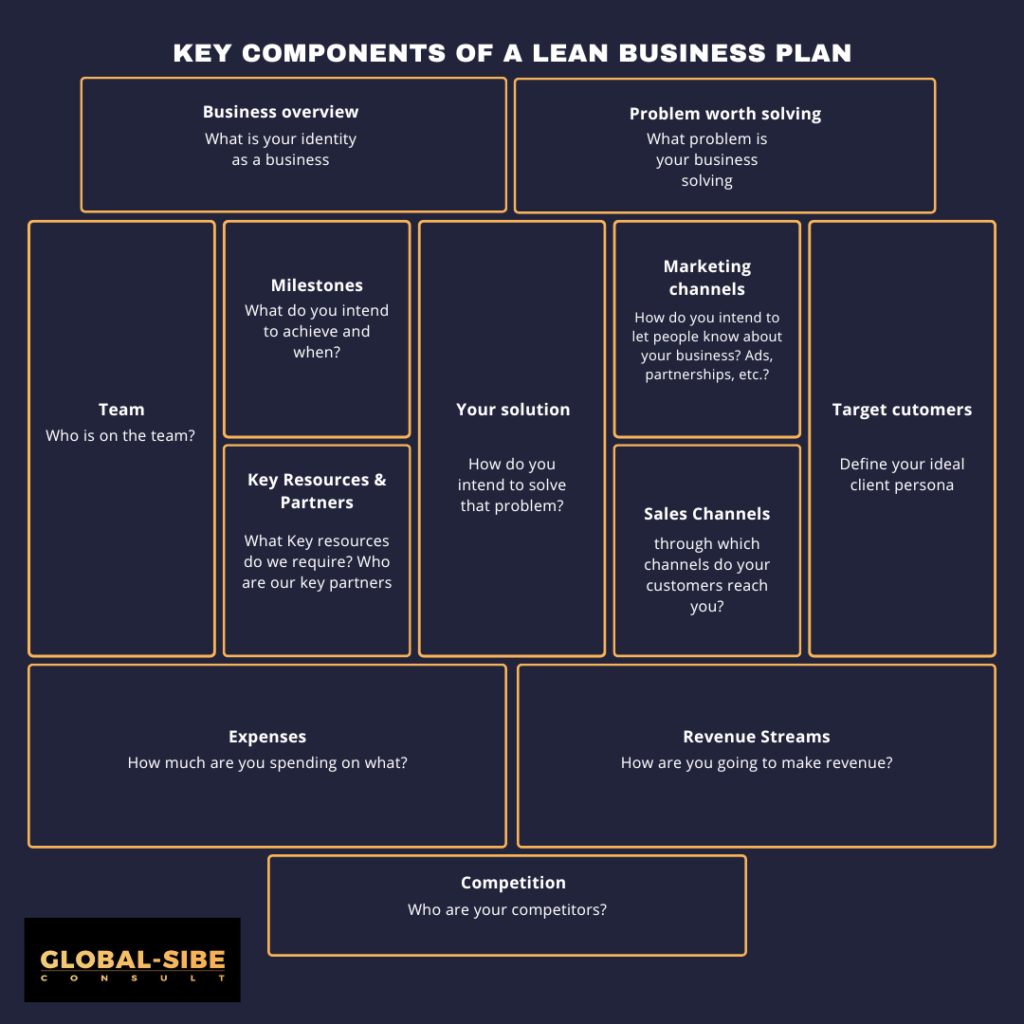
1. Create Your Plan
To get started, consider the following essential elements that should be included in your lean business plan:
- Your business strategy
- Your business tactics
- Your business model
- A schedule
- Forecast and budget
a. Define your Business Strategy
At the heart of your lean business plan is a clear articulation of your business strategy. Start by addressing these fundamental aspects:
I. The Problem Your Business Intends to Solve
Clearly state the problem your business intends to solve. Identify the pain points of your target customers and how your product or service addresses these issues. A concise and focused problem statement will guide your business in the right direction.
For example, let’s say you’re launching a meal kit delivery service for busy professionals. Your problem statement could be, “Our business aims to solve the time constraints faced by professionals by providing convenient, healthy, and ready-to-cook meal kits delivered to their doorstep.”
II. Your Ideal Customer
Understanding your target audience is fundamental to your business’s success. Define your ideal customer persona, including demographics, preferences, and pain points. This knowledge will enable you to tailor your product or service to cater to their specific needs.
In our meal kit delivery service example, the ideal customer persona could be “urban professionals aged 25-40, with disposable income, seeking healthy and time-saving meal options.”

III. Your Competitors
Conduct a competitive analysis to identify your main competitors and understand their strengths and weaknesses. This analysis will provide insights into differentiating your offering and positioning your business effectively.
b. State Your Business Tactics
The next thing to do after defining your business strategy is to state how you intend to execute it. Meaning you will be thinking about outlining your sales plan, marketing strategies, and the key team members who will drive your business forward.
I. Sales Plan
Outline your sales strategy and tactics, including how you will attract and retain customers. Will you be selling online or will you have a physical storefront? Perhaps you will sell through both channels. Make it clear how customers can locate you to get your products or services.
II. Marketing Strategies
If you are a startup, then no one probably knows you exist except maybe those close to you, and that is why you need marketing to get the word out about your business. If you are an existing business, then how do you intend to boost your marketing? Define your marketing channels and campaigns that will create awareness and drive customer acquisition.
III. Your Team
Behind every successful business, there is a team of brilliant people pulling the strings to make it work. If you are a startup, then you probably need to build a team. Briefly introduce the key members of your team and their roles in supporting your business objectives.
IV. Partners and Resources
Due to the nature of your business, you may need to partner with suppliers or distributors to have smooth business operations. Who are these other businesses, and what resources do you currently have at your disposal? What do you need to buy? Identify potential partners and resources that can contribute to your business’s success and state them.
c. Define Your Business Model
Describe how your business intends to generate revenue and achieve profitability. This section should include pricing models, revenue streams, and any cost-saving strategies you plan to implement. For instance, some businesses generate revenue using the subscription model. Others do this by using freemium. The most important thing is that you settle on a model that best fits your services or products and brings in the most revenue.
d. Forecast and Budget
Forecasting is like trying to catch a glimpse of the future. Since it’s almost impossible to see the future, the best you can do is use numbers to predict what the future of your business will look like. Forecasting and budgeting is another great way to find out if your business idea is feasible.
Here, you will have to develop a detailed financial forecast that projects your business’s income and expenses over a specific period. How much do you see your business bringing in over that period of time, and how much do you intend to spend on your business? If you have different products or services under your business, you should forecast how much each product or service category is going to bring in over that period.
Doing this will help you understand the financial viability of your venture, so you can make informed decisions about resource allocation.
e. Create a Schedule
The last thing to do when creating your plan is to set clear milestones and timelines for your business’s key activities. Having a well-defined schedule will help you stay on track and measure your progress effectively.
For example, if you are a startup operating an e-commerce business, then when will your website be up and running? When will you officially lunch, and when will you run your first marketing campaign?
If you are an established business, then your schedule should revolve around when the key activities of your strategy will be implemented.
Your schedule should also state who is responsible for what and at what time that activity is supposed to be completed. Make sure to hold your team accountable in order for your schedule to go smoothly.
2. Test Your Plan
With your lean business plan in hand, it’s time to put your ideas to the test. Your lean business plan is based only on assumptions about your business idea, especially if you are a startup with very limited data about your target audience. And you will have to test those assumptions to see if they are true or false.
As stated earlier, one of the main reasons why people use lean business plans is that they allow you to quickly test your idea or business model in a limited capacity to see if it’s viable.
So in the testing phase, launch your product or service in a limited capacity to gather real-world feedback from your target audience. This validation process will provide invaluable insights and help you refine your business model until you find one that works well.
If you are an existing business, you test by implementing your newly crafted strategies to see if they bring better results than your previous results.
3. Review the Results
Now most of the information you will need to make informed decisions, like changing your business model, is in the result. Hence, critically analyzing the result is important for your business’s success.
Do you need to change your business model? Is the business idea worth investing resources in? Is your pricing right? Will you be able to meet your target revenue? All of the answers to these questions are in the result of your test. Analyze the results, considering both successes and failures. Identify areas for improvement, and use this feedback to iterate and enhance your business strategies.

4. Revise Your Plan
Based on the lessons learned during testing and review, update your lean business plan accordingly. Remember, the lean business planning approach is a process. It’s all about finding strategies and implementing those strategies to see if they yield better results. Hence, you shouldn’t be afraid to go back to the drawing board to find out why a particular strategy didn’t work or why it worked so well.
Remember, the key to success lies not just in planning but also in continuous adaptation and improvement.
Will I Need a Traditional Business Plan After the Lean Business Plan?
There is no doubt that a lean business plan is an excellent tool for getting your business off the ground quickly and efficiently. However, there may be situations where a more detailed traditional business plan is necessary, especially when seeking funding from investors.
Investors often require a comprehensive understanding of your business, including detailed financial projections, market analysis, and long-term strategies. While a lean business plan serves as a solid foundation, having a traditional business plan can demonstrate your commitment and vision to potential investors.
Additionally, creating a detailed internal business plan can be beneficial for your internal team and other stakeholders. It provides a comprehensive view of your business and fosters alignment among team members, fostering a shared sense of purpose and direction.